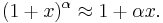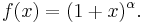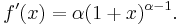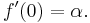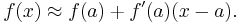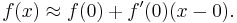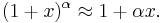Binomial approximation
The binomial approximation is useful for approximately calculating powers of numbers close to 1. It states that if  is a real number close to 0 and
is a real number close to 0 and 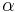 is a real number, then
is a real number, then
This approximation can be obtained by using the binomial theorem and ignoring the terms beyond the first two.
The left-hand side of this relation is always greater than or equal to the right-hand side for 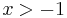 and
and 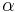 a non-negative integer, by Bernoulli's inequality.
a non-negative integer, by Bernoulli's inequality.
Derivation using Mellin Transform
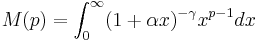
- Let
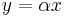
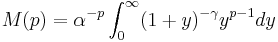
- Let y=z/(1-z)
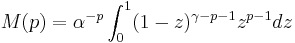
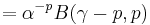
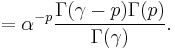
Using the inverse Mellin transform:
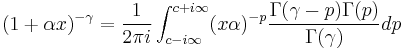
Closing this integral to the left, which converges for 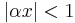 , we get:
, we get:
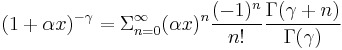
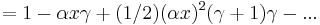
Derivation using Linear Approximation
When x = 0:
Using linear approximation: